Respiratory System:
In the Respiratory System there are four main organs called:
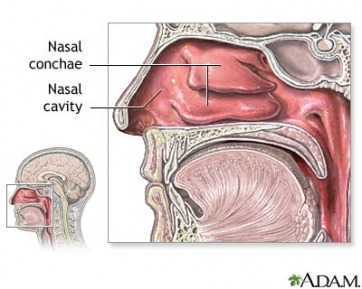
Air pollution can affect our respiratory system by entering the main route for pollutants which is through the nose, mouth and throat. The nose is the most common place where pollutants exist. The nose is very efficient at trapping and holding inhaled pollutants, because of the sticky substance in the nose. This substance is called Mucus, and it is very good at trapping pollutants which enter our nose. Pollutants build up and accumulate inside the nose and can cause problems in the sinuses or can be absorbed in mucus membranes. The cell damage caused by exposure to pollutants puts the body's defence system on alert. The body then initiates an inflammatory response. This can make the body more susceptible to disease. It can also trigger a secondary response causing the release of various chemicals or breakdown of products. For example, when the nose is exposed to ozone, the airways are burned, causing inflammation and mucus production. The inflamed, runny nose has an increased sensitivity and is more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections.
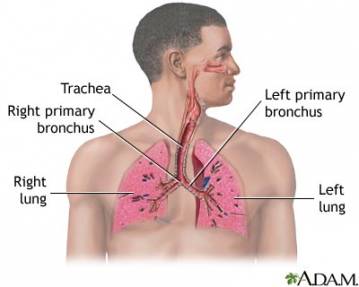
Air pollution can result in an increase in deaths and hospital admissions due to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Ground-level ozone, nitrogen oxide and airborne particles are the main sources of air pollution. All three are oxidants. When oxidant air pollutants enter our respiratory system, cell damage occurs causing inflammation and making cells more vulnerable to cancer. Severe inflammation can cause significant damage including scarring of lung tissue, called fibrosis, and abnormal thickening. These disorders make breathing more difficult. Nitrogen oxide impairs the infection-fighting ability of white blood cells in the alveoli which is the thin walled sacs at the end of the bronchi deep in the lung and it may increase the risk of lung infections.
Exposure to toxic chemicals from incinerators, power plants, mining operations and other industrial facilities also have been linked to lung cancer. Volatile organic compounds, nitrogen-containing and halogenated organics, PAH's (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), toxic metals and many by products of incomplete combustion are all potential carcinogens that pollute the air. Getting these dangerous chemicals in our systems can often lead to damaged cells, making them more vulnerable to cancer and other carcinogens.
- Nose
- Lungs
- Throat
- Mouth
Air pollution can affect our respiratory system by entering the main route for pollutants which is through the nose, mouth and throat. The nose is the most common place where pollutants exist. The nose is very efficient at trapping and holding inhaled pollutants, because of the sticky substance in the nose. This substance is called Mucus, and it is very good at trapping pollutants which enter our nose. Pollutants build up and accumulate inside the nose and can cause problems in the sinuses or can be absorbed in mucus membranes. The cell damage caused by exposure to pollutants puts the body's defence system on alert. The body then initiates an inflammatory response. This can make the body more susceptible to disease. It can also trigger a secondary response causing the release of various chemicals or breakdown of products. For example, when the nose is exposed to ozone, the airways are burned, causing inflammation and mucus production. The inflamed, runny nose has an increased sensitivity and is more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections.
Air pollution can result in an increase in deaths and hospital admissions due to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Ground-level ozone, nitrogen oxide and airborne particles are the main sources of air pollution. All three are oxidants. When oxidant air pollutants enter our respiratory system, cell damage occurs causing inflammation and making cells more vulnerable to cancer. Severe inflammation can cause significant damage including scarring of lung tissue, called fibrosis, and abnormal thickening. These disorders make breathing more difficult. Nitrogen oxide impairs the infection-fighting ability of white blood cells in the alveoli which is the thin walled sacs at the end of the bronchi deep in the lung and it may increase the risk of lung infections.
Exposure to toxic chemicals from incinerators, power plants, mining operations and other industrial facilities also have been linked to lung cancer. Volatile organic compounds, nitrogen-containing and halogenated organics, PAH's (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), toxic metals and many by products of incomplete combustion are all potential carcinogens that pollute the air. Getting these dangerous chemicals in our systems can often lead to damaged cells, making them more vulnerable to cancer and other carcinogens.
Definitions:
Ozone: It is a colorless gas: it can be found up in the Stratosphere and it protects us from Ultraviolet radiation. (It acts as a screen)
Nitrogen Oxide: It is formed by nitric acid on Oxidizable materials, and it is present in car exhausts.
Oxidant: It is a substance that oxidizes another substance.
Fibrosis: It is the formation of fibrous tissue and it occurs as a reactive process.
Alveoli: Is the thin walled sacs at the end of the bronchi deep in the lung.
Carcinogen: It is something that produces cancer.
Halogenated Organics: It is a type of pollutant in our environment, it is dangerous to human health, it bio-degrades very slowly, and it is commonly used. An example is the pesticide DDT.
Poly-cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Known as PAH's. They are able to mix very easily with oil and water and are commonly found in our air. They occur in oil, coal, tar deposits and fuel burning. If ingested they are very harmful to our body.
Ozone: It is a colorless gas: it can be found up in the Stratosphere and it protects us from Ultraviolet radiation. (It acts as a screen)
Nitrogen Oxide: It is formed by nitric acid on Oxidizable materials, and it is present in car exhausts.
Oxidant: It is a substance that oxidizes another substance.
Fibrosis: It is the formation of fibrous tissue and it occurs as a reactive process.
Alveoli: Is the thin walled sacs at the end of the bronchi deep in the lung.
Carcinogen: It is something that produces cancer.
Halogenated Organics: It is a type of pollutant in our environment, it is dangerous to human health, it bio-degrades very slowly, and it is commonly used. An example is the pesticide DDT.
Poly-cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Known as PAH's. They are able to mix very easily with oil and water and are commonly found in our air. They occur in oil, coal, tar deposits and fuel burning. If ingested they are very harmful to our body.